Alright folks, let's dive right into it! If you're here, chances are you've stumbled upon the term "integer" and you're wondering what the heck it really means. Well, buckle up because we're about to break it down in a way that even your grandma could understand. Integers are more than just numbers—they’re the building blocks of math, and today, we’re going to explore everything you need to know about them. So, grab a snack, get comfy, and let’s get started!
Now, you might be thinking, "Why do I even need to know about integers? I’m not a mathematician!" But here's the thing: integers pop up everywhere in real life. Whether you're counting your coins, tracking your bank balance, or measuring temperature changes, integers are right there with you. They’re simple yet powerful, and once you understand them, you’ll start seeing them everywhere!
Before we go any further, let’s set the stage. This article isn’t just another boring textbook explanation. We’re going to explore integers from the ground up, breaking them down into bite-sized pieces that are easy to digest. By the end of this, you’ll not only know what an integer is but also how to use them like a pro. So, are you ready to level up your math game? Let’s do this!
Read also:Emily Carriveau Divorce Filing
Table of Contents
Integer Basics: Breaking It Down
Integer Operations: Adding, Subtracting, Multiplying, and Dividing
Real-Life Examples of Integers
Read also:Xnnn
Common Mistakes People Make with Integers
Applications of Integers in Technology
Wrapping It Up: Why Integers Matter
What is an Integer?
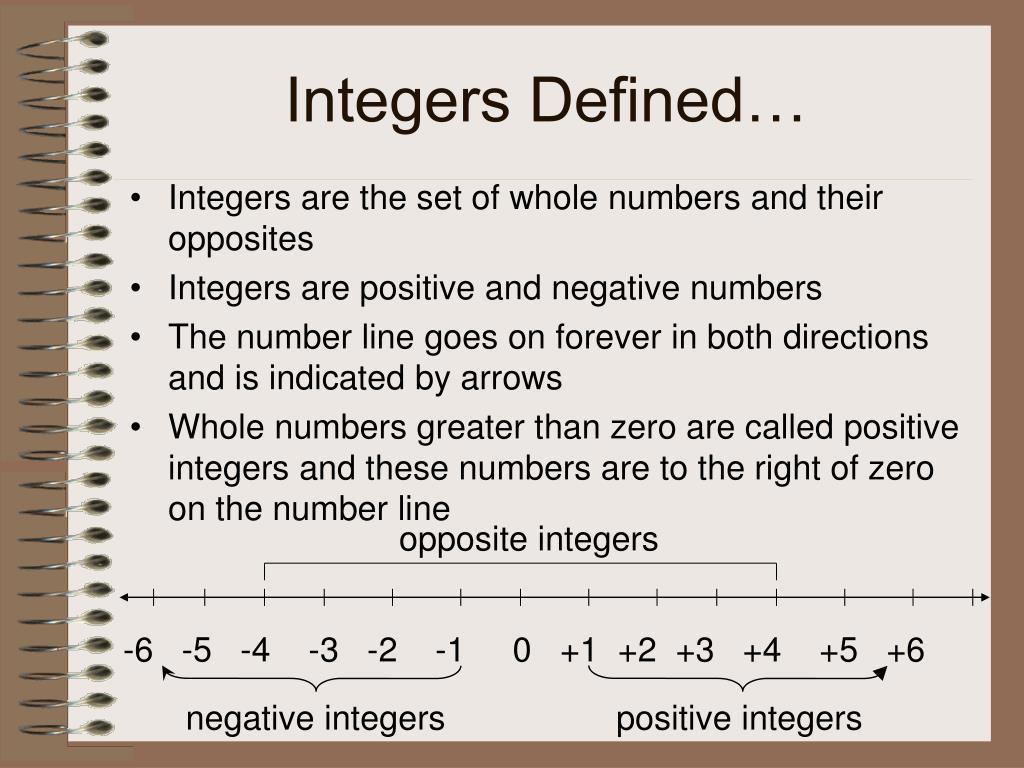
Alright, let’s start with the basics. An integer is simply a whole number that can be positive, negative, or zero. No fractions, no decimals—just clean, straightforward numbers. Think of integers as the VIPs of the number world. They’re the ones you can count on without worrying about pesky decimal points or fractions messing things up.
For example, if you have 5 apples, that’s an integer. If you owe someone 3 dollars, that’s also an integer (just a negative one). And if you have exactly zero cookies left in the jar? Yep, that’s an integer too!
Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Positive integers: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5…
- Negative integers: -1, -2, -3, -4, -5…
- Zero: 0 (it’s special because it’s neither positive nor negative)
Why Are Integers Important?
Integers are like the unsung heroes of mathematics. They’re used in everything from basic arithmetic to advanced computer programming. Without integers, we wouldn’t be able to count, calculate, or even navigate the digital world. They’re the foundation of so many things we take for granted every day.
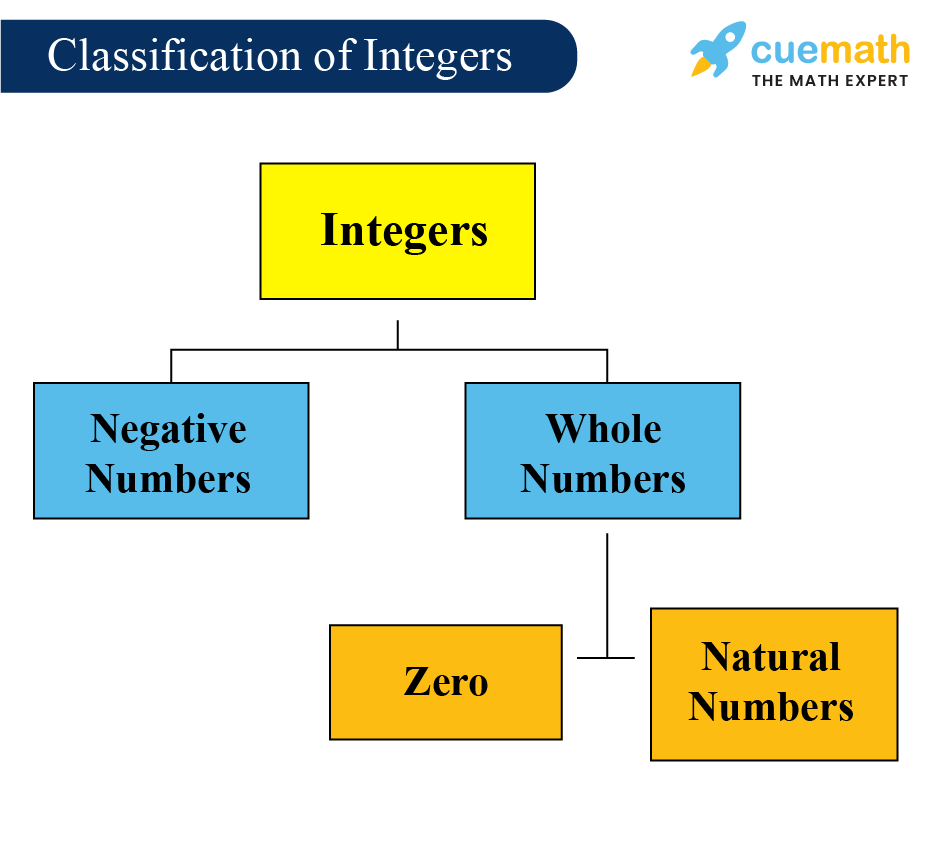
Types of Integers
Now that we know what integers are, let’s break them down into their different types. There are three main categories:
Positive Integers
These are the numbers you’re probably most familiar with. They’re the ones you use for counting: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and so on. Positive integers are always greater than zero, and they’re often used to represent quantities like money, people, or objects.
Negative Integers
Negative integers are like the dark side of the number world. They’re less than zero and are used to represent things like debt, temperature below zero, or even scores in a game. Think of them as the opposite of positive integers.
Zero
Zero is a special integer because it’s neither positive nor negative. It’s like the neutral zone in the number world. Zero is incredibly important because it acts as a placeholder in our number system and helps us understand concepts like nothingness or balance.
Integer Basics: Breaking It Down
Let’s take a closer look at how integers work. At its core, an integer is any number that doesn’t have a fractional or decimal component. This means that numbers like 7, -12, and 0 are all integers, while numbers like 3.5 or 1/2 are not.
Here’s a fun fact: integers are part of a larger group called rational numbers. Rational numbers include all integers, fractions, and decimals that can be expressed as a ratio of two integers. But don’t worry—we’ll save that for another day!
How Do Integers Relate to Other Number Systems?
Integers are a subset of real numbers, which also include fractions, decimals, and irrational numbers. They’re like the middle child in the number family—important, but not as flashy as some of their siblings.
Integer Operations: Adding, Subtracting, Multiplying, and Dividing
Now that we know what integers are, let’s talk about what you can do with them. The four basic operations—addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division—are the bread and butter of integer math. Here’s a quick rundown:
Addition
Adding integers is pretty straightforward. If the signs are the same, you add the numbers and keep the sign. If the signs are different, you subtract the smaller number from the larger one and take the sign of the larger number.
Subtraction
Subtracting integers is just like adding them, but with a twist. When you subtract a negative integer, it’s the same as adding its positive counterpart. For example, 5 - (-3) is the same as 5 + 3.
Multiplication
Multiplying integers is where things get interesting. If the signs are the same, the result is positive. If the signs are different, the result is negative. For example, (-4) × (-3) = 12, but (-4) × 3 = -12.
Division
Dividing integers works the same way as multiplication. If the signs are the same, the result is positive. If the signs are different, the result is negative. Just remember to watch out for division by zero—it’s a big no-no in math!
Real-Life Examples of Integers
Integers aren’t just abstract concepts—they’re all around us in everyday life. Here are a few examples:
- Bank balances: If you have $500 in your account, that’s a positive integer. If you’re overdrawn by $100, that’s a negative integer.
- Temperature: When it’s -5 degrees Celsius outside, that’s a negative integer. If it’s 25 degrees, that’s a positive integer.
- Altitude: Mountain heights are positive integers, while depths below sea level are negative integers.
Properties of Integers
Integers have some cool properties that make them behave in predictable ways. Here are a few:
Closure Property
When you add, subtract, or multiply two integers, the result is always another integer. This is called the closure property.
Commutative Property
You can add or multiply integers in any order without changing the result. For example, 3 + 5 = 5 + 3 and 2 × 4 = 4 × 2.
Associative Property
You can group integers in different ways when adding or multiplying without changing the result. For example, (2 + 3) + 4 = 2 + (3 + 4).
Distributive Property
This property allows you to distribute multiplication over addition. For example, 2 × (3 + 4) = (2 × 3) + (2 × 4).
Common Mistakes People Make with Integers
Even the best of us make mistakes when working with integers. Here are a few common ones to watch out for:
- Forgetting the sign: When adding or subtracting integers, it’s easy to lose track of the signs. Always double-check your work!
- Dividing by zero: This is a big no-no in math. Division by zero is undefined, so avoid it at all costs.
- Multiplying signs incorrectly: Remember, two negatives make a positive, but a negative and a positive make a negative.
A Brief History of Integers
Integers have been around for thousands of years. The ancient Egyptians and Babylonians used integers for counting and measuring, while the Greeks and Romans developed more advanced systems for working with them. Fast forward to today, and integers are an essential part of modern mathematics and computer science.
Applications of Integers in Technology
Integers aren’t just for math class—they’re also a crucial part of technology. Here are a few examples:
- Programming: Integers are used in almost every programming language to store and manipulate data.
- Data Storage: Computers use integers to represent everything from text to images to sound.
- Cryptography: Integers are used in encryption algorithms to keep our data safe online.
Wrapping It Up: Why Integers Matter
And there you have it—a comprehensive guide to understanding integers. From their basic definition to their real-world applications, integers are an essential part of our daily lives. Whether you’re balancing your checkbook, coding a new app, or just counting your steps, integers are right there with you.
So, what’s next? Why not test your newfound knowledge by trying out some integer problems? Or, if you’re feeling adventurous, dive deeper into the world of mathematics and explore topics like fractions, decimals, and irrational numbers. The possibilities are endless!
Before you go, don’t forget to leave a comment and let us know what you thought of this article. And if you found it helpful, be sure to share it with your friends. Together, we can make math fun and accessible for everyone!